Reduce Environmental Impact

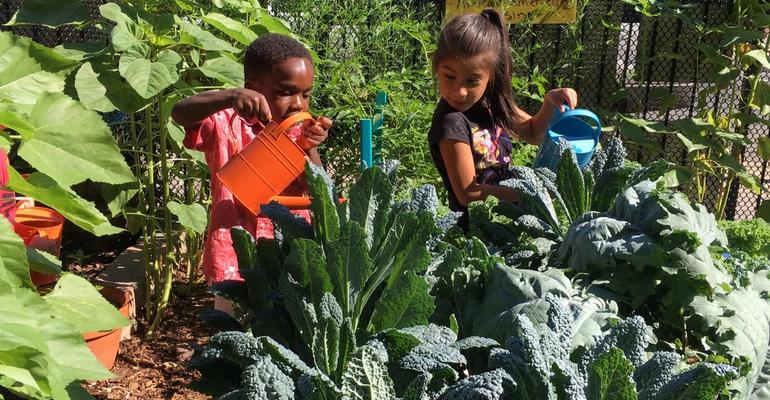
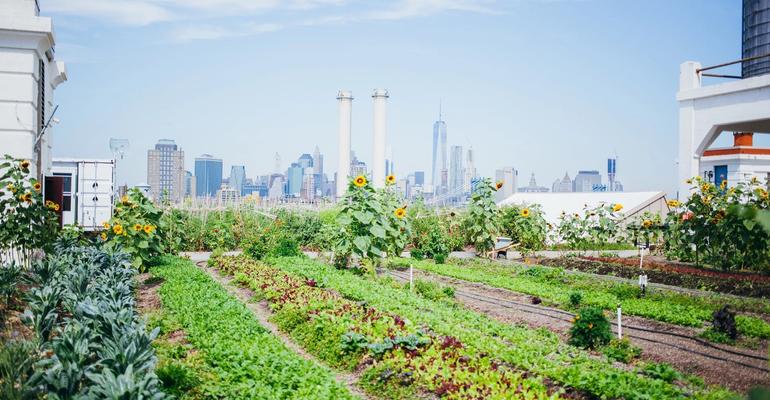
Sustainable farms and food businesses build healthy ecosystems by improving soil health, increasing biodiversity, and reducing the carbon and water footprint of food production, while advancing public health and worker safety. By promoting climate-friendly diets and providing robust markets for sustainable food producers, institutions can reduce their environmental impact and support the adoption of sustainable farming, ranching, and business practices.
Strategies

Reduce beef and other meat purchases
By replacing some meat purchases with plant proteins—and focusing on regenerative ranching for remaining meat products—institutions can significantly lower their carbon and water footprint.

Reduce dairy purchases
Institutions can contribute to a healthier planet by shifting towards plant proteins and sustainably-produced foods.

Replace conventional produce with organic
Growing produce without synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and herbicides reduces toxic exposure for farmworkers and nearby communities, conserves water, captures carbon in the soil, and fosters biodiversity.
Explore Your Impact With Our Calculators
Carbon and Water Calculator
Pesticides Calculator
Replacing conventionally-produced animal products with plant proteins could also:

Reduce the amount of farm animals raised without humane living conditions.
Reduce the public health burden of living near industrial animal production facilities.

Reduce the harmful effects of concentrated animal feeding operations that disproportionately impact rural communities and communities of color.
Reducing pesticide use could also:

Improve working conditions for farmworkers who currently lack federal protections from workplace hazards.

Protect children from health and developmental risks caused by prenatal and childhood pesticide exposure.
Real-World Examples
Learn about more ways to advance good food policies in your community.





